It is no secret that we want to get rid of cairo as the drawing API in GTK, so we can move more of our drawing onto the GPU.
While People have found creative ways to draw things with render nodes, they don’t provide a comprehensive drawing API like Skia or, yes, cairo. Not a very satisfying state of affairs.
A few years ago, we started to investigate how to change this, by making paths available as first-class objects in GTK. This effort is finally starting to come to fruition, and you can see the first results in GTK 4.13.0.
Paths
So, what is a path? A rough definition could be:
A sequence of line segments or curves that may or may not be connected at their endpoints.
When we say curves, we specifically mean quadratic or cubic Bézier curves. On top of cairo, we also support rational quadratic Béziers (or as Skia calls them: conics), since they let us model circles and rounded rectangles precisely.
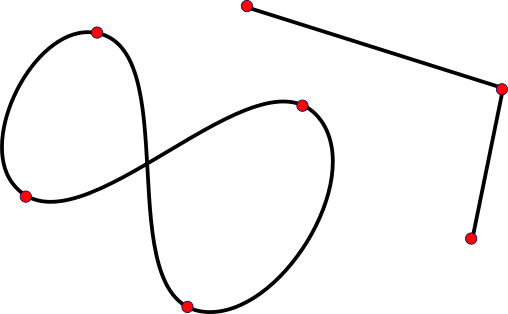 This picture shows a typical path, consisting of 4 curves and 2 lines, some of which are connected. As you can see, paths can be closed (like the 4 curves here) or open (like the 2 lines), with a start- and endpoint.
This picture shows a typical path, consisting of 4 curves and 2 lines, some of which are connected. As you can see, paths can be closed (like the 4 curves here) or open (like the 2 lines), with a start- and endpoint.
And how are paths useful for drawing? First, you can use a path to define an area (the part that’s inside the path) and fill it with a color, a gradient or some more complex content.
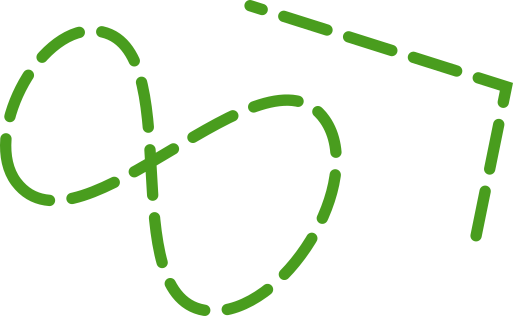
 Alternatively, you can stroke the path with various properties such as line width, color or dash pattern.
Alternatively, you can stroke the path with various properties such as line width, color or dash pattern.
 Paths in GTK
Paths in GTK
The object that we use for paths in GTK is GskPath. It is a compact, immutable representation that is optimized for rendering. To create a GskPath, you need to use a GskPathBuilder, which has many convenience methods to create paths, either from individual curves or from predefined shapes.
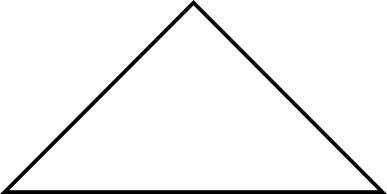
This example creates a path that is a closed triangle:
builder = gsk_path_builder_new (); gsk_path_builder_move_to (builder, 0, 50); gsk_path_builder_line_to (builder, 100, 50); gsk_path_builder_line_to (builder, 50, 0); gsk_path_builder_close (builder); path = gsk_path_builder_free_to_path (builder);
 And this one creates a circular path with the given center and radius:
And this one creates a circular path with the given center and radius:
builder = gsk_path_builder_new (); gsk_path_builder_add_circle (builder, center, radius); path = gsk_path_builder_free_to_path (builder);
Outlook
In the next post, we’ll look at properties of paths, and how to query them.